Introduction
The relationship between India and Russia is a tapestry woven with threads of historical camaraderie, strategic cooperation, and mutual respect. Rooted in the Cold War era, this partnership has evolved into a multifaceted alliance that spans political, economic, defense, and cultural domains.
As two nations with rich histories and diverse cultures, India and Russia have fostered a bond that transcends mere diplomatic ties, reflecting a shared vision for a multipolar world order and a commitment to global peace and stability. This enduring partnership continues to adapt to the changing geopolitical landscape, underscoring the importance of collaboration in addressing contemporary challenges and opportunities.
What kind of country is Russia?
Russia, the world’s largest country by land area, is a nation of vast contrasts and significant geopolitical influence. Here are some important points about Russia:
- Geography: Russia spans across two continents, Europe and Asia, and covers eleven time zones. It has the world’s fourth-longest coastline and is bordered by sixteen sovereign nations.
- Population: With a population of approximately 145 million people, Russia is the ninth-most populous country globally¹.
- Economy: Russia’s economy is diverse, with key sectors including energy, manufacturing, and agriculture. It is known for its vast natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas.
- Politics: The country operates under a federal semi-presidential constitutional republic. The President of Russia is the head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of government.
- Culture: Russian culture is rich and varied, with a long history of contributions to literature, music, ballet, and the arts. The Russian language is one of the six official languages of the United Nations.
- Military: Russia maintains one of the largest military forces in the world and has been a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since its inception.

brief History
The historical background of India-Soviet Union relations is quite extensive and marked by cooperation and mutual support, especially during the Cold War era.

- 1947: Diplomatic relations were established between India and the Soviet Union following India’s independence. The USSR opened its embassy in New Delhi on April 12, 1947.
- 1950s: Relations warmed up after Stalin’s death, with the USSR supporting India in various international disputes, including the Kashmir issue. Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru visited the Soviet Union in 1955, and First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev reciprocated later that year.
- 1960s: The Soviet Union provided substantial economic and military assistance to India. In 1962, despite the Sino-Indian War, the USSR declared neutrality but continued to support India.
- 1971: The signing of a friendship treaty further solidified the relationship between the two nations.
- 1991: The dissolution of the Soviet Union marked the end of this chapter in bilateral relations. However, the legacy of their partnership continued to influence India’s foreign policy and relations with Russia.
This relationship was characterized by strategic cooperation in political, economic, and defense spheres, with the Soviet Union playing a significant role in India’s development during that period.
Important ISSUES in India Russia relations
Under the leadership of Vladimir Putin, Russia-India relations have continued to evolve, reflecting both historical ties and contemporary geopolitical dynamics.

1. Strategic Partnership: The relationship between Russia and India has been described as an “all-weather” partnership, with both countries maintaining a strategic alliance. The strategic partnership between India and Russia is a comprehensive and multifaceted relationship that has evolved over many years. It is traditionally built on five major components:
- Politics: Both nations support the creation of a multipolar world order and share a special relationship in international terms.
- Defence: India is the second largest market for the Russian defence industry, with a significant portion of its military hardware imports coming from Russia.
- Civil Nuclear Energy: The two countries collaborate in the field of civil nuclear energy, with Russia being one of the key suppliers of nuclear technology to India.
- Anti-Terrorism Cooperation: They work together to combat terrorism and ensure regional security.
- Space Exploration: Advancement and exploration of outer space travel is another area of cooperation.
These components are supported by various agreements and collaborations, reflecting the depth and breadth of the strategic partnership between India and Russia. The relationship is also characterized by mutual respect and shared interests in maintaining global stability and peace.
2.Defence Cooperation: Russia remains a significant supplier of military equipment to India, although there has been a shift towards diversification in India’s defense procurement. The arms trade between Russia and India has been a cornerstone of their strategic partnership. Here are some key points:
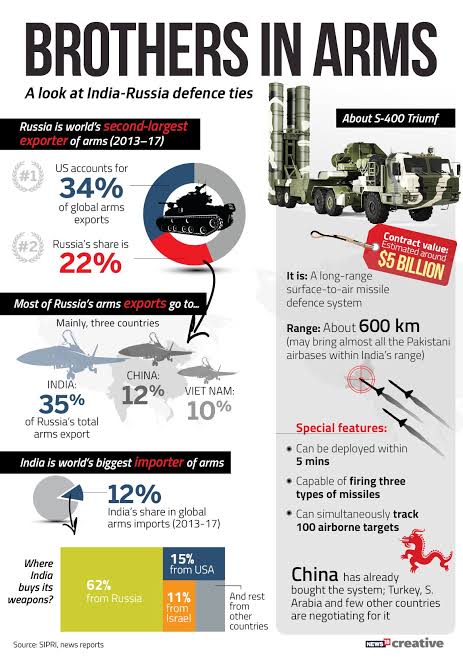
- Historical Context: Traditionally, India has been one of the largest importers of arms from Russia, with Russian-made equipment forming a significant part of the Indian Armed Forces’ arsenal.
- Recent Trends: Despite a decline in Russia’s share of Indian defence imports from 62% to 45% between 2017-2022, Russia continues to be India’s largest arms supplier. This decrease is attributed to India’s efforts to diversify its arms imports and boost domestic manufacturing.
- Competition: France has emerged as a strong competitor, with its defence exports to India increasing by 489% between 2013-17 and 2018-22, making it the second-largest supplier after Russia.
- Strategic Importance: The arms trade remains a vital aspect of the bilateral relationship, with India not joining Western sanctions on Russia, thereby demonstrating its independent foreign policy.
- Future Outlook: The two countries have signed agreements to reinforce their military and technical cooperation until 2031 and aim to boost annual trade to $30 billion by 2025.
These points highlight the evolving dynamics of the arms trade between Russia and India, reflecting both historical ties and contemporary geopolitical shifts.
3. Economic Ties: Despite global economic challenges, Russia and India have sought to strengthen their economic cooperation.
The economic and trade relations between India and Russia have seen significant developments over the years. Here are some key statistical data points:
- Bilateral Trade Volume: In the financial year 2022-23, the bilateral trade between India and Russia amounted to US$ 49.36 billion. Indian exports to Russia were US$ 3.14 billion, while imports from Russia were US$ 46.21 billion.
- Trade Growth: During April-May 2023-24, India’s trade with Russia saw a remarkable increment of 161.22% compared to the same period in the previous year.
- Export Composition: Major items exported from India to Russia include drug formulations, biologicals, residual chemical and allied products, iron and steel, marine products, bulk drugs and drug intermediates, coffee, etc. In the period from April-November 2023-24, major exports included iron and steel, pharmaceutical products, organic chemicals, marine products, coffee, tea, mate, and spices.
- Import Composition: Major items imported by India from Russia include petroleum (crude), coal, coke, and briquettes, fertilizers manufacturers, petroleum products, pearl, precious and semi-precious stones, vegetable oils, etc. In the period from April-November 2023-24, major imports included mineral fuels, mineral oils and products of their distillation, animal or vegetable fats and oils, fertilizers manufacturers, pearl, precious and semi-precious stones.
These statistics reflect the growing economic ties between the two nations and highlight areas of mutual interest and cooperation.
4. Geopolitical Considerations: The changing geopolitical landscape, including India’s growing ties with the US and its participation in the Quad, has introduced new complexities into the bilateral relationship.
The relationship between India and Russia holds significant geopolitical importance due to several factors:
- Strategic Autonomy: India’s partnership with Russia allows it to maintain strategic autonomy, especially in the context of its relations with other major powers.
- Military Cooperation: Russia is a major supplier of military equipment to India, which is crucial for India’s defense capabilities.
- Energy Security: Russia is a key partner for India in terms of energy security, providing natural gas and nuclear energy cooperation².
- Balancing Act: India’s relationship with Russia helps it balance its ties with other countries, including the United States and China.
- Historical Ties: The long-standing historical ties between India and Russia provide a foundation for cooperation in various international forums.
- Economic Interests: Bilateral trade and investment are important economic interests for both countries, with efforts to increase trade volume and investment.
These aspects underscore the multifaceted nature of the India-Russia relationship and its relevance in the current geopolitical landscape.
Recent Developments
India has urged Russia to return its citizens recruited by the Russian army after two were killed in Ukraine. This incident highlights the ongoing tensions and challenges within the broader context of international relations.
Recent developments in the relationship between India and Russia have been marked by a shift in dynamics, particularly in light of the geopolitical changes following the Ukraine War. Here are some key points:
- Diplomatic Engagement: India’s External Affairs Minister Subrahmanyam Jaishankar’s visit to Moscow signified a turning point, as India appeared to turn the page on ties with Russia after two years of tightrope walking.
- Trade and Energy: Despite the global context, India has continued to import oil and coal from Russia in significant quantities. However, there has been a focus on diversifying trade and energy sources.
- Strategic Autonomy: India has maintained its strategic autonomy by not joining Western sanctions on Russia, demonstrating its independent foreign policy.
- Military Cooperation: The arms trade remains a crucial aspect of the bilateral relationship, with Russia being a major supplier of military equipment to India².
- Economic Interests: Both countries have expressed interest in building an international political and economic system that is open and fair for everyone.
These developments reflect the evolving nature of the India-Russia relationship in response to changing global circumstances.
Conclusion
Overall, while the foundational elements of the Russia-India relationship remain strong, both countries are navigating a complex international environment that requires careful diplomacy and strategic decision-making.
In conclusion, the relationship between India and Russia stands as a testament to the enduring nature of strategic partnerships. Despite the shifting sands of global politics, the bond between these two nations remains resilient, grounded in a foundation of trust and shared interests. As they navigate the complexities of the 21st century, fostering resilience, open communication, and a shared commitment to global peace will be pivotal in determining the success of their relations in the years ahead. The future of India-Russia ties will undoubtedly be shaped by their ability to adapt to changing circumstances while upholding the principles that have long defined their partnership.